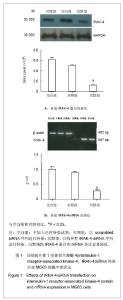
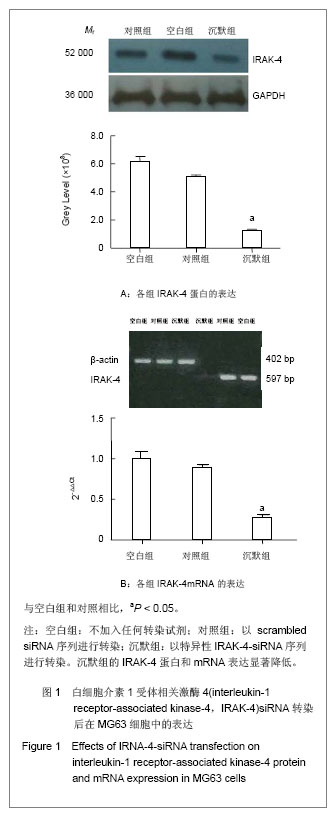
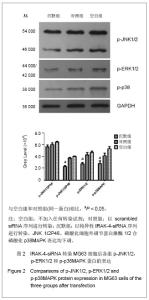
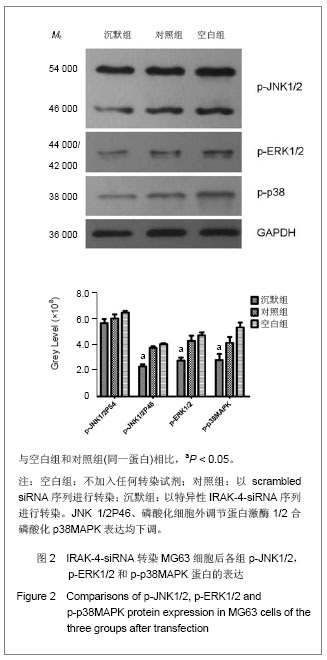
| [1]Levine BR, Hsu AR, Skipor AK, et al. Ten-year outcome of serum metal ion levels after primary total hip arthroplasty: a concise follow-up of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(6):512-518.
[2]Ikeda Y, Tajima S, Izawa-Ishizawa Y, et al. Estrogen regulates hepcidin expression via GPR30-BMP6-dependent signaling in hepatocytes. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40465.
[3]Stephens AS, Stephens SR, Hobbs C, et al. Myocyte enhancer factor 2c, an osteoblast transcription factor identified by dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-enhanced mineralization. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(34):30071-30086.
[4]Takanashi M, Oikawa K, Sudo K, et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by siRNA cream in an arthritis model mouse. Gene Ther. 2009;16(8):982-989.
[5]Kwan TS, Padrines M, Théoleyre S, et al. IL-6, RANKL, TNF-alpha/IL-1: interrelations in bone resorption pathophysiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15(1): 49-60.
[6]Yang SY, Zhang K, Bai L, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate and titanium alloy particles activate peripheral monocytes during periprosthetic inflammation and osteolysis. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(5):781-786.
[7]Harrison JC, Zyla TR, Bardes ES, et al. Stress-specific activation mechanisms for the “cell integrity” MAPK pathway. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(4):2616-2622.
[8]Suzuki N, Suzuki S, Duncan GS, et al. Severe impairment of interleukin-1 and Toll-like receptor signaling in mice lacking IRAK-4. Nature. 2002;416(6882):750-756.
[9]Vandrovcova M, Hanus J, Drabik M, et al. Effect of different surface nanoroughness of titanium dioxide films on the growth of human osteoblast-like MG63 cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(4):1016-1032.
[10]Zhao H, Dong W, Zheng Y, et al. The structural and biological properties of hydroxyapatite-modified titanate nanowire scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2011;32(25):5837-5846.
[11]Schwartz Z, Bell BF, Wang L, et al. Beta-1 integrins mediate substrate dependent effects of 1alpha,25(OH)2D3 on osteoblasts. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;103(3-5): 606-609.
[12]Vallés G, García-Cimbrelo E, Vilaboa N. Involvement of extracellular Hsp72 in wear particle-mediated osteolysis. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(3):1146-1155.
[13]Ma GK, Chiu R, Huang Z, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate particle exposure causes changes in p38 MAPK and TGF-beta signaling in differentiating MC3T3-E1 cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94(1):234-240.
[14]Baud V, Liu ZG, Bennett B, et al. Signaling by proinflammatory cytokines: oligomerization of TRAF2 and TRAF6 is sufficient for JNK and IKK activation and target gene induction via an amino-terminal effector domain. Genes Dev.1999;13(10): 1297-1308.
[15]Ming X. Cellular delivery of siRNA and antisense oligonucleotides via receptor-mediated endocytosis. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011;8(4):435-449.
[16]Samuel-Abraham S, Leonard JN. Staying on message:design principles for controlling nonspecific responses to siRNA. FEBS J. 2010;277(23):4828-4836.
[17]Kim YH, Park JW, Patel C, et al. Polyethylene Wear and Osteolysis After Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty with Alumina-on-Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene Bearings in Patients Younger Than Thirty Years of Age. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(12):1088-1093.
[18]Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780-785.
[19]Haynes DR, Crotti TN, Zreiqat H. Regulation of osteoclast activity in peri-implant tissues. Biomaterials. 2004;25(20): 4877-4885.
[20]Stashenko P, Dewhirst FE, Peros WJ, et al. Synergistic interactions between interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and lymphotoxin in bone resorption. J Immunol. 1987;138(5): 1464-1468.
[21]Chen X, Zhu G, Jin T, et al. Cadmium stimulates the osteoclastic differentiation of RAW264.7 cells in presence of osteoblasts. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012;146(3):349-353.
[22]Lye E, Mirtsos C, Suzuki N, et al. The role of interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase-4 (IRAK-4) kinase activity in IRAK-4-mediated signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(39): 40653-40658.
[23]Kyo F, Futani H, Matsui K, et al. Endogenous interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor alpha, contributes to the development of toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88-mediated acute arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(8):2530-2540.
[24]Johnson GL, Lapadat R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science. 2002;298(5600):1911-1912.
[25]Song, KW, Talamas FX, Suttmann RT, et al. The kinase activities of interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase (IRAK)-1 and 4 are redundant in the control of in?ammatory cytokine expression in human cells. Mol Immunol. 2009;46(7): 1458-1466.
[26]Koziczak-Holbro M, Littlewood-Evans A, Pöllinger B, et al. The critical role of kinase activity of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 in animal models of joint inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(6):1661-1671.
[27]Yang Z, Huang B, Zhang Z, et al. Effects of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 gene silencing on human osteoblast-like cells. Connect Tissue Res. 2012;53(6): 498-507.
[28]Olmedo ML, Landry PS, Sadasivan KK, et al. Regulation of osteoblast levels during bone healing. J Orthop Trauma. 1999;13(5):356-362.
[29]Hipskind RA, Bilbe G. MAP kinase signaling cascades and gene expression in osteoblasts. Front Biosci.1998;3: d804-816.
[30]Lai CF, Chaudhary L, Fausto A, et al. Erk is essential for growth, differentiation, integrin expression, and cell function in human osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(17): 14443-14450. |